The 2015 planning season is upon us. It’s the time of year when the C-Suite is busy sharpening their elbows to ready themselves for the budget brawl. To help arm marketers for this blood bath, I’ve pulled together benchmarks and/or research needed to defend and win marketing dollars. Here are some answers, and sources, for your five toughest budget questions.
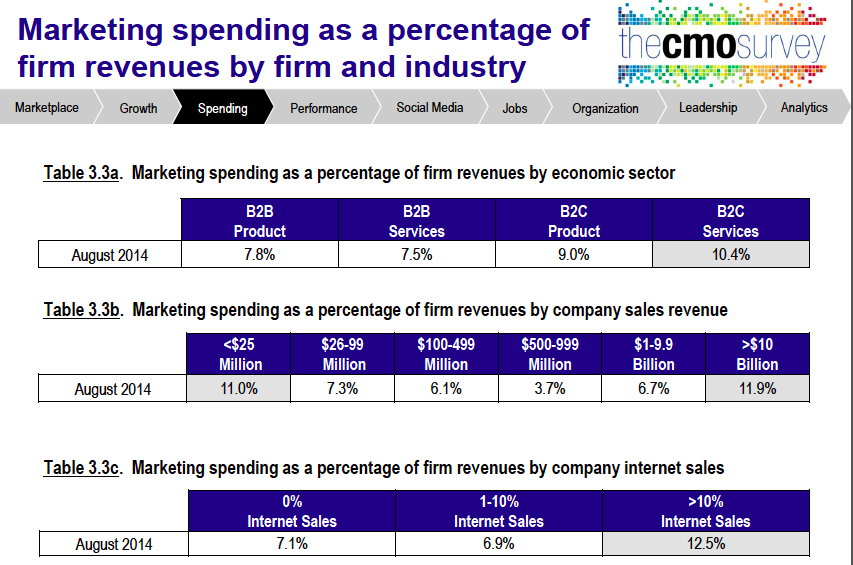
- How much should we be spending on marketing? It’s a classic question and a favorite of CEO’s everywhere. The mere mention of it is enough to stop marketers in their tracks. Fortunately, the AMA, McKinsey and the Duke Fuqua School of Business have got your back with their 2014 CMO Survey. Section 3 of the report contains data from 350 marketers on their spending from digital to people and programs. The research even breaks spending out by size of company, type of company (B2B or B2C, and B2B products or services). The report is packed with valuable information — it’s a “must have” for any marketer this year.
- What should the mix between people and programs? This question comes shortly, if not immediately, after the question above. Ten years ago the general benchmark ratio was 40/60, forty percent of the budget went to staff and the remaining to program spending. Now it’s the reverse, 60/40 people to program spending, for a number of reasons. The biggest factor has been the need for specific skill sets that are in high demand relating to analytics, social media and content marketing have driven up staff cost. Need more information, here’s a useful infographic on the real cost of social media, including salary cost for staff.
- Where should we invest? Typically, this is a teaser question, and could also be asked as; “if you had an incremental $1 (or $10K, $100K, etc.) where would you invest it?” Keep in mind that just because the CEO is asking the question doesn’t necessarily mean you’ll get the incremental funding, but you better be able to answer the question. To do that see IBM’s C-Suite Priorities report entitled The Customer-activate Enterprise. The research, collected from face to face interviews with over 4000 senior executives, provides insights into the priorities of each member of the C-Suite. The top priority in the report is Digital. Including everything from increasing responsiveness to customers, to making the organization more agile and responsive. Specific priorities for CMO’s, it’s about capturing; analyzing and using customer data across touch points.
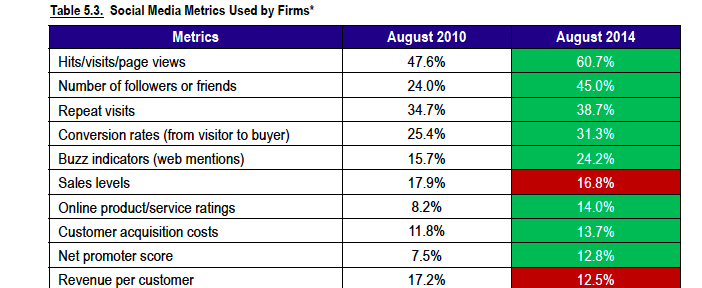
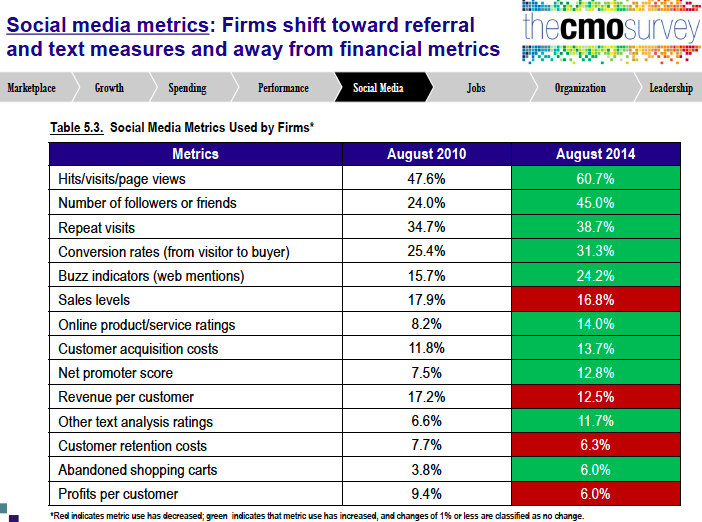
- What’s the payoff/return/business impact of Social Media? There are a number of sources that you could tab into to help develop a response. I’ve always been a fan of HubSpot’s State-of-Inbound. Additionally, if you have downloaded the CMO Study mentioned in bullet #1, there is a whole section on Social Media (see graphic). Interestingly enough after four years “Visits” and “Followers/Friends” are still the leading social media metrics today. Personally, I’m not a fan, try using measurements related to engagement. Note the gains being made in “Conversion Rates” and “Buzz Indicators” over that last four years. This is the result of the development of better measurement tools. Here’s a great cheat sheet from SocialMediaToday on the Top 50 Tools. For digital and mobile benchmarks download Adobe Digital Index’s Best of the Best Report.
- What return should we expect from our marketing investments? This is a loaded question. Recognize that what the executive really wants to know is: “What will marketing do for me and/or my group?” As a result, answer the question based on their area of interest, and in their language. If it’s a sales executive, talk in terms of new leads, customers and pipeline value. If it’s the CEO, talk about brand value, revenue growth or customer retention or loyalty. Rarely is this question asked on behalf of the organization as a whole. Even more rare, is the executive that believes the numbers you’ve quantitatively derived for a ROI.
Lastly, go in strong and ask for a bigger budget. Here’s a report to keep in your back pocket in case you need it, Gartner’s CMO Spend 2015: Eye on the Buyer. The report will support your request for an increase, and maybe help the “powers that be” understand that if you’re not getting a bigger budget, your key competitors probably are…now go get ‘em!